光电化学系列讲座(二十七) 2010-10-11
中国可再生能源学会、光化学委员会光电化学系列讲座(二十七):
报告人:李嫕 教授
中国科学院理化技术研究所 光化学转换与功能材料重点实验室
李嫕 研究员,中科院理化技术研究所研究员,博士生导师。1985年毕业于北京大学化学系,获理学学士学位,1988年北京理工大学获硕士学位,1994年中科院感光化学研究所获博士学位。1996-1999年,美国依利诺伊大学厄巴拿-香槟分校化学系从事博士后研究工作。现任所学位委员会副主任、所青年科学技术委员会委员、中国科学院光化学转换与功能材料重点实验室副主任,中国化学会光化学专业委员会委员;J. Photochem. Photobiol. A:Chemistry编委,“Pertanika Journal of Science and Technology”杂志国际顾问委员会委员。多年来一直从事分子和超分子体系的光物理和光化学研究,设计合成构建了多种分子和超分子体系,并对分子和超分子体系中的光物理和光化学性质进行研究。在J. Am. Chem. Soc.等国内外学术刊物上发表研究论文七十余篇,研究成果受到国内外同行关注。
报告题目:树枝形聚合物体系中电子转移和能量传递研究
内容提要:
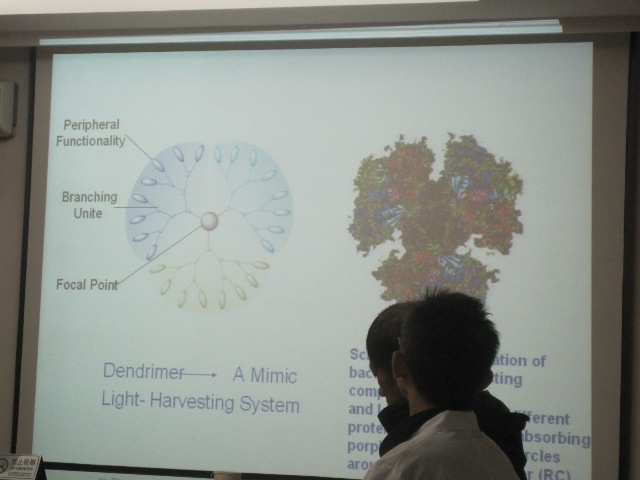
Studies on natural photosynthetic systems have revealed that the structure of the photosynthetic unit is a central reaction center surrounded by light-harvesting complexes. The remarkable character of the photosynthetic system is that the energy of any photon absorbed by antenna complexes is transferred to the reaction center and converted into a chemical potential with unit efficiency. In the process of photochemical conversion, the photoinduced electron/energy transfer process plays an important role and has been inspiring intense studies. Dendrimers are regularly and hierarchically branched synthetic macromolecules with numerous chain ends all emanating from a single core. The chromophores can be accurately located at the core, focal point, periphery, or even at each branching point of the dendritic structure. The specific structure of the dendrimer makes it a mimic light-harvesting system, where the antenna chromophores surround the central reaction center. In this presentation, recent advances in my group of light-harvesting dendrimers will be discussed, emphasizing the energy transfer and electron transfer characteristics in these systems.
